
Instead, it is reflected through the accumulated depreciation account, which is a contra-asset account that offsets the corresponding asset’s original cost. Understanding how carrying cost and market value differ helps businesses make informed decisions about asset management, such as when to sell or replace an asset. It also ensures financial statements accurately reflect the true economic value of assets. In short, recording accumulated depreciation keeps your books accurate and ensures that your financial statements reflect the true value of your assets over time.

Automating Cash Application: Faster Matching, Faster Cash Flow

Accruing tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid. This is important for accurate financial reporting and compliance with… In each case the fixed assets journal entries show the debit and credit account together with a brief narrative. For a fuller explanation of journal entries, view our examples section.
Adjusting Journal Entries Accounting Student Guide
However, the company’s cash reserve is not impacted by the recording as depreciation is a non-cash item. Therefore, the cash balance would have been reduced at the time of the acquisition of the asset. A reduction in the value of tangible fixed assets due to normal usage, wear and tear, new technology or unfavourable market conditions is called Depreciation. Whether you maintain the provision for depreciation/accumulated depreciation account determines how to do the journal entry for depreciation. The journal entry is a debit to Depreciation Expense and a credit to the contra asset Accumulated Depreciation. Crediting Accumulated Depreciation increases the total amount of depreciation recognized against the asset to date.
- This article will discuss the more common types with a journal entry example for each depreciation type.
- Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping.
- In accounting, making the right journal entries for depreciation is crucial.
- Companies need to account for the depreciation expense to adhere to the matching principle in accounting, which states that expenses should be matched with revenues.
- By systematically allocating the cost of assets, businesses can ensure their books reflect a true and fair view of their financial position.
- A loss on disposal will reduce net income, while a gain on disposal will increase it.
How do changes in useful life or salvage value impact a depreciation journal entry?
These adjustments are crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial reporting and providing stakeholders with a true picture of the company’s asset values. Since the depreciation journal entry is a fundamental concept in financial accounting. The primary reason for this is to ensure that the cost of the asset is aligned with the income that it generates for the business. Journal entries for depreciation are necessary to record the decrease in the value of fixed assets over time. The Depreciation Expense Account is debited, while the Accumulated Depreciation Account is credited.
- This accounting method spreads the asset’s purchase cost across the periods it helps generate revenue, rather than tracking fluctuations in market value.
- Examples of PP&E include buildings, machinery, equipment, and vehicles.
- Find the answers to commonly asked questions about depreciation journal entries.
- It’s a common misconception that depreciation is a form of expensing a capital asset over many years.
- Therefore, you need to select the right way of passing the correct type of depreciation journal entry example.
- Once the new estimates are determined, the remaining book value of the asset is spread over the revised useful life.
How to Record Depreciation Journal Entry: With Examples

The accumulated depreciation account is a contra asset account that is used to reduce the carrying value of the asset on the balance sheet. Due to such reasons, it’s important for businesses to accurately record the depreciation of fixed assets. Yes, depreciation of fixed assets is recorded in the accounting records of a business. The cost of tangible assets is spread over a period of time according to their useful life.
The annual depreciation expense is the actual dollar amount of depreciation that is recorded each year. Recording depreciation requires a journal entry based on double-entry bookkeeping, where total debits equal total credits. This entry is typically made as an adjusting entry at the end of an accounting period (monthly, quarterly, or annually) before preparing financial statements. Businesses owning Accounting Periods and Methods long-term assets like equipment or buildings must account for their gradual loss of value through a process called depreciation. Recording depreciation ensures financial statements accurately reflect an asset’s worth and the company’s profitability over time. It’s the same basic idea as with machinery, but now we’re applying it to things you use in your office.

Using the Wrong Depreciation Method
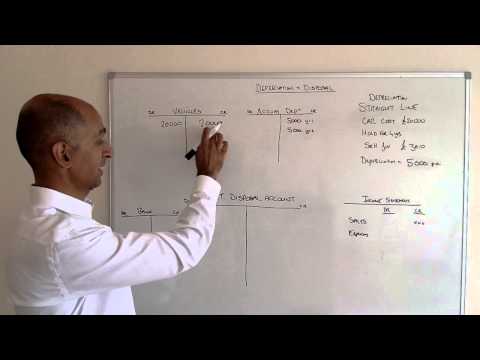
Recording depreciation has direct effects on a company’s primary financial statements, providing a more accurate picture of its financial position and performance. On the income statement, Depreciation Expense journal entry for depreciation is recognized as an operating expense. This expense reduces a company’s net income, which, in turn, lowers its taxable income. The reduction in net income reflects the portion of the asset’s cost consumed during the period.
- Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of a tangible fixed asset over its useful life.
- Depreciation of fixed assets journal entry is Debit the Depreciation Account and Credit Corresponding Fixed Asset Account.
- It is important to note that all expenses incurred for the construction of the building are added to the cost of the building.
- However, the percentage rate used in the double declining balance method is twice the rate used in the declining balance method.
- Every time you make a depreciation entry, you add to the accrued depreciation account.
- It accounts for the wear and tear, obsolescence, or other factors that reduce an asset’s value over time.
The Accounting Accounts Involved
A depreciation journal entry is important because it helps businesses adhere to the matching principle and the accounting standards. This entry is made at the end of each accounting period as part of the adjusting entries process. Recording depreciation in this manner ensures that the asset’s usage is recognized as an expense, while its carrying value on the balance Mental Health Billing sheet is systematically reduced over time. When a fixed asset is purchased, it is initially recorded on the balance sheet as an asset.
